Bitcoin , the top cryptocurrency by market capitalization, is retreating following the recent Fed rate reduction. This decline may stem from the Fed’s communication, which has left traders anxious about future monetary easing.
The Fed on Wednesday reduced the benchmark interest rate by 25 basis points to 3.25% as anticipated and stated it will start buying short-term Treasury bills to manage banking system liquidity.
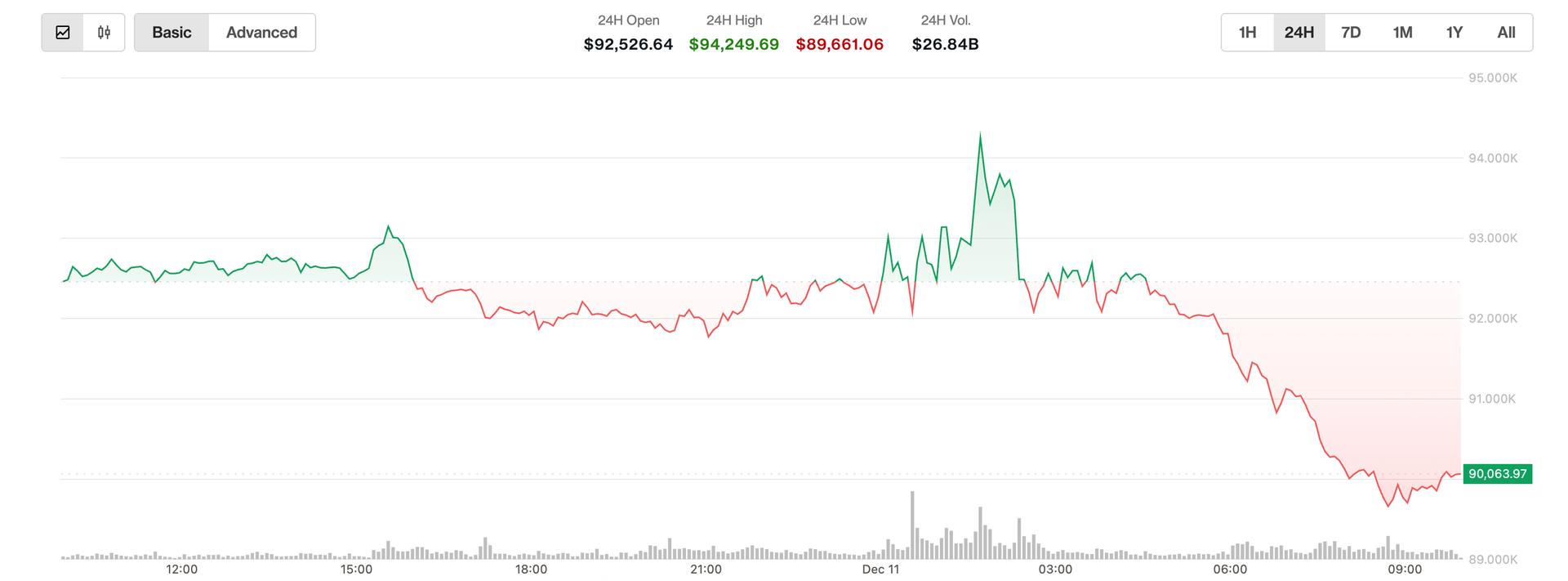
At the time of reporting, BTC was trading under $90,000, marking a 2.4% drop since the early Asian trading hours, according to CoinDesk data. Ether fell by 4% to $3,190, with the CoinDesk 20 Index also down over 4%.
This risk-averse behavior likely results from increasing indications of internal divisions within the Fed regarding the balance between controlling inflation and achieving employment goals, alongside signals complicating future rate cut paths.
Two members voted against any change on Wednesday, with individual forecasts indicating that six FOMC members deemed a cut “inappropriate.”
Furthermore, the central bank hinted at just one more rate cut by 2026, disappointing expectations for two to three cuts.
“There is division within the Fed, and the market lacks clarity on the prospective path of rates until May 2026, when Chairman Jerome Powell will be succeeded. The appointment of a Trump loyalist, likely to push for more aggressive rate cuts, may serve as a clear signal for rate policies. However, there are still six months ahead,” stated Greg Magadini, director of derivatives at Amberdata, speaking to CoinDesk.
He further remarked that a necessary “deleveraging” or downswing seems likely to persuade the Fed of the need for lower rates decisively.
Shiliang Tang, managing partner of Monarq Asset Management, noted that BTC is moving downward alongside the stock market.
“Crypto markets initially surged on the announcement but have consistently declined since, mirroring stock market futures, with BTC repeatedly failing to surpass the local high of $94k for the third time in two weeks,” Tang shared with CoinDesk.
He added that the implied volatility continues to decrease, with the last significant market catalyst of the year now behind us.
Liquidity management, not QE
Although the crypto community has promptly labeled the Fed’s reserve management initiative as a revival of traditional quantitative easing (QE), which spurred unprecedented risk-taking in 2020-21, that interpretation may not be accurate.
The reserve management initiative consists of the Fed buying $40 billion in short-term Treasury bills. Although this does expand its balance sheet, it primarily aims to address liquidity pressures in money markets without committing to sustained balance-sheet enlargement or yield suppression.
Traditional QE focused on long-duration Treasuries and mortgage-backed securities to aggressively decrease long-term yields and infuse trillions into the economy, directly enhancing liquidity for speculative investments.
Andreas Steno Larsen, Founder of Steno Research, articulated the situation succinctly on X, stating, “This is sadly not Lambo QE. More like ‘my Uber is 7 minutes away’ QE.”
Some analysts contend that the current program is a preventative measure against possible instability in money markets akin to that of 2019.
“Rather than risking a 2019-style scramble, the Fed is discreetly buying a buffer now. Essentially, it’s the Fed ensuring the financial system has sufficient breathing space to navigate through the spring without any disruptions,” noted pseudonymous observer EndGame Macro.